Physiotherapy, Osteopathy or Chiropractic Care?
Which Is Right For You?
Have you ever wondered, what’s the difference between physio, osteo, and chiro? You’re not alone; it’s a very common question. You might be suffering from an injury right now and you aren’t sure which to see. The following is a short primer on physios, osteo, and chiro.
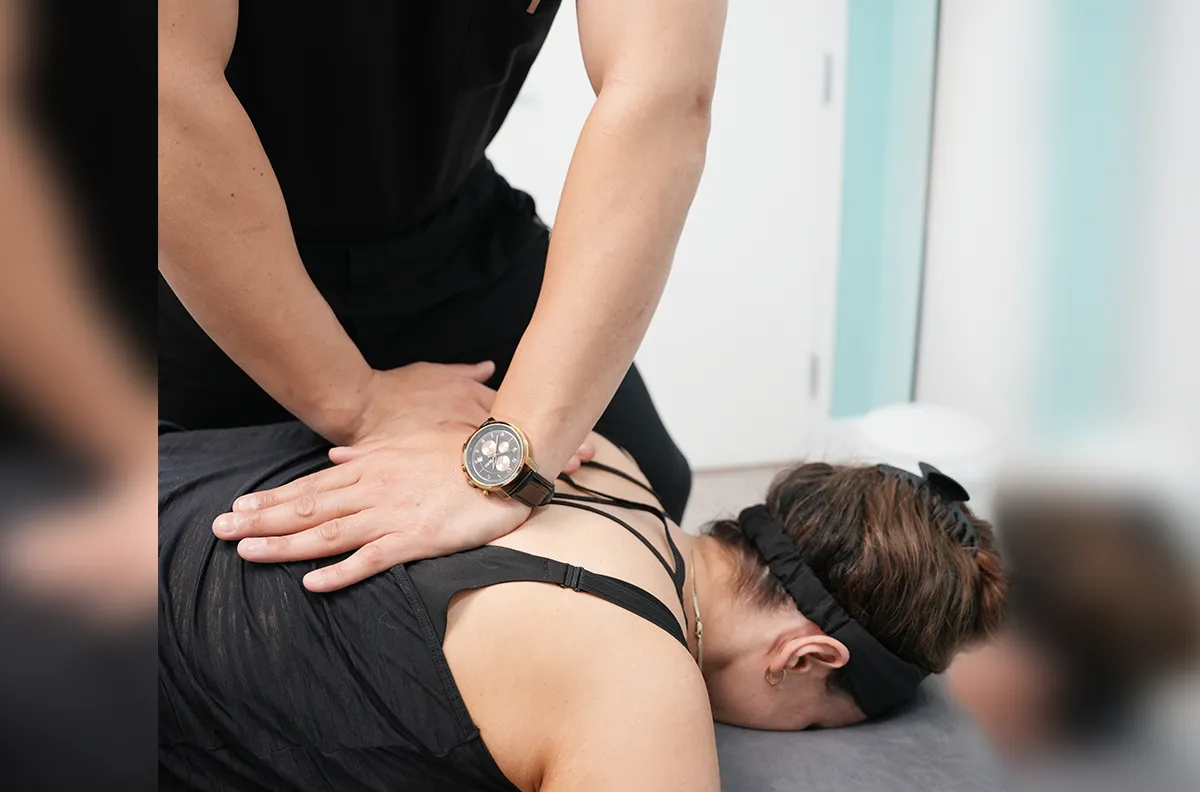

What Do Chiropractors Do?
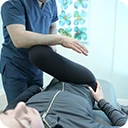
Chiropractic is concerned with the prevention, maintenance, and repair of musculoskeletal and spinal injuries. Chiropractors believe that the nervous system controls all bodily functions and gives the body the ability to self-heal. If your nervous system is fully functioning, the body will self-regulate itself. Chiropractors adjust the spine to correct poor nerve transmission to help your body move freely and to improve your general health. A lot of chiropractic is about prevention and maintaining health. Chiropractors will commonly recommend diet, exercise, and healthy lifestyle choices.
What’s A Chiropractic Session Like?
A normal chiropractic session will involve three things: a consultation, a body examination, and an adjustment.
During the consultation, expect to answer a number of questions relating to pain such as when the pain started, how the pain started, where the pain is located, and what the pain feels like.
The body exam involves reflex and orthopedic assessments that test muscle strength, muscle tone, and range of motion. If the chiropractor believes an adjustment is safe and appropriate, they will perform one.
How Does Chiropractic Help?
Chiropractors treat many issues including:
Back and neck pain
Headaches and migraines
Sciatica
Disc injuries
Arthritis
Whiplash
Discomfort during pregnancy
Sports injuries
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Chronic fatigue
Scoliosis
Plantar fasciitis
Digestive issues
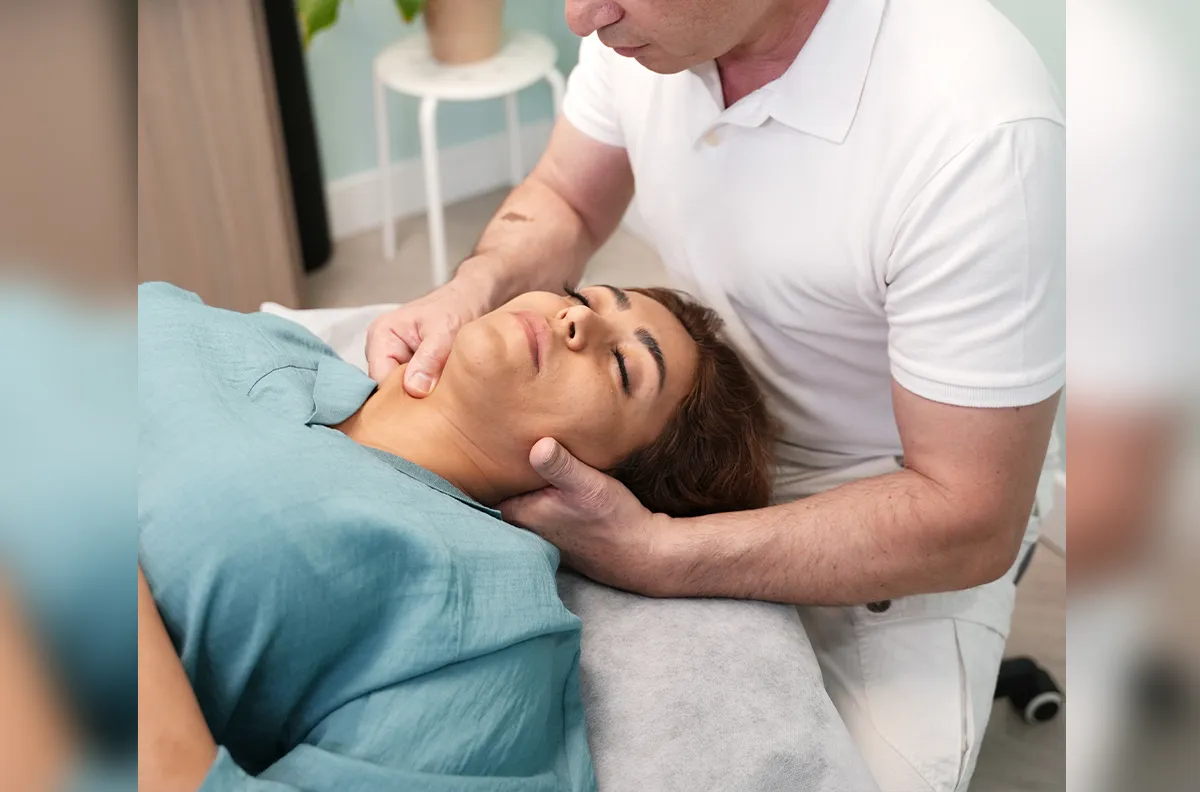
What Do Osteopaths Do?
Osteopaths treat musculoskeletal problems by moving, stretching and massaging a person’s muscles and joints. Osteopaths are similar to chiropractors in that they believe good health is dependent on a well-functioning spine. Osteopaths avoid drugs or surgery unless absolutely necessary.
Although they share similarities to chiropractors, osteopathic treatments differ in that they focus more on a body’s soft tissues.
What’s An Osteopathic Session Like?
An osteopath begins with a consultation to learn about a patient’s symptoms and medical history.
They will then perform a thorough exam of the afflicted area. Because of osteopathy’s holistic view, the osteopath may examine other parts of the body as well. If your knee hurts, your osteopath may take a look at your back, pelvis, and ankle. They may also ask about your work habits, exercise routine, or diet. Osteopaths will then offer a diagnosis. They’ll treat the patient and advise them on how to self-manage their condition.
How Does Osteopathy Help?
Osteopaths treat many issues including:
Lower back pain
Neck pain
Sports injuries
Chronic pain in bones, joints or muscles
Headaches and migraines
Pelvic pain
The physical effects of cerebral palsy
Arthritis, bursitis, and tendonitis
Women’s health issues
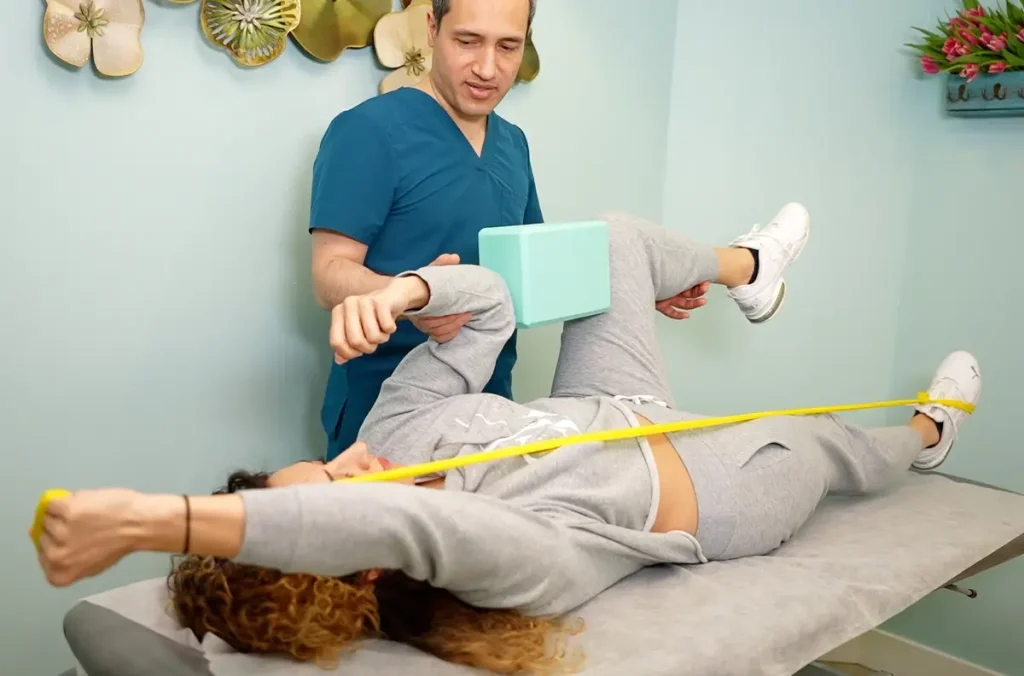

What Do Physiotherapists Do?
Physiotherapists specialize in preventing injury and loss of movement. Physiotherapists frequently act as consultants in business settings to improve workplace ergonomics and reduce the chance of repetitive stress disorder and lower back pain. Physiotherapists frequently treat athletes and equip them exercise programs aimed at preventing repetitive strain.
Two common physiotherapy treatments are exercise and mobility training. In addition to manual therapy, physiotherapists also teach patients how to perform certain exercises on their own. Physiotherapists may also mobilize a joint or perform muscle massage to encourage proper function and movement.
What’s A Physiotherapy Session Like?
A physio session begins with an assessment to find out where the injury is, how it occurred, and how it’s affecting everyday life.
Following this assessment, a physiotherapist will perform movement tests and assess the muscles and surrounding structures before treating the injury. The patient is then given a timeline of how to manage the injury as well as a recovery exercise plan.
How Does Physiotherapy Help
Physiotherapists treat many issues
including:
Strength and conditioning
Injury prevention
Muscle pain and stiffness
Sports injuries
Work injuries
Sprains and strains
Spinal dysfunction
Arthritis
Share it to some how needs to know it